1. Introduction
Cyber attacks have become one of the most significant threats to businesses, governments, and individuals worldwide. No organisation is immune—whether it’s a small business, a global corporation, or critical infrastructure. Attackers continuously evolve their tactics, leveraging new technologies like AI, automation, and zero-day exploits to bypass traditional security measures.
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of cyber attack types, real-world case studies, defensive strategies, emerging trends, and most importantly—how to architect a resilient security framework that can withstand modern threats.
2. Types of Cyber Attacks
A. Malware-Based Attacks
Malware remains one of the most common and damaging cyber threats. Ransomware, for example, encrypts critical files and demands payment for decryption, as seen in the Colonial Pipeline attack (2021), which disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S. East Coast. Trojans, disguised as legitimate software, can steal sensitive data, while worms self-replicate across networks, causing widespread damage like the Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iranian nuclear facilities.
B. Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering exploits human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Phishing—fraudulent emails pretending to be from trusted sources—remains highly effective, accounting for 90% of data breaches. More sophisticated variants include spear phishing, which targets high-profile individuals, and deepfake scams, where AI-generated voice or video impersonations trick victims into transferring money or revealing credentials.
C. Network & Infrastructure Attacks
Network-based attacks aim to disrupt services or steal data. DDoS attacks overwhelm servers with traffic, making websites inaccessible—attackers often use botnets like Mirai, which hijacks IoT devices. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks intercept communications, while DNS spoofing redirects users to malicious sites without their knowledge.
D. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are long-term, stealthy attacks typically conducted by nation-states. The SolarWinds breach (2020), attributed to Russian hackers, infiltrated thousands of organisations via a compromised software update, remaining undetected for months.
E. Supply Chain Attacks
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in third-party vendors. The 2020 SolarWinds hack demonstrated how a single compromised supplier could impact countless organisations. Similarly, the MOVEit Transfer breach (2023) exposed data from banks, airlines, and government agencies.
F. Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day attacks target undisclosed software vulnerabilities. The Log4j flaw (2021), for instance, allowed hackers to execute remote code on millions of systems before a patch was available.
3. Modern Cybersecurity Architecture: The Blueprint for Defense
Why Architecture Matters
Traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses are obsolete in today’s cloud-first, remote-work world. Modern cybersecurity requires an integrated, layered architecture that provides:
- Visibility across all systems
- Automated protection against known and unknown threats
- Resilience to contain breaches when they occur
The Cybersecurity Architecture Framework
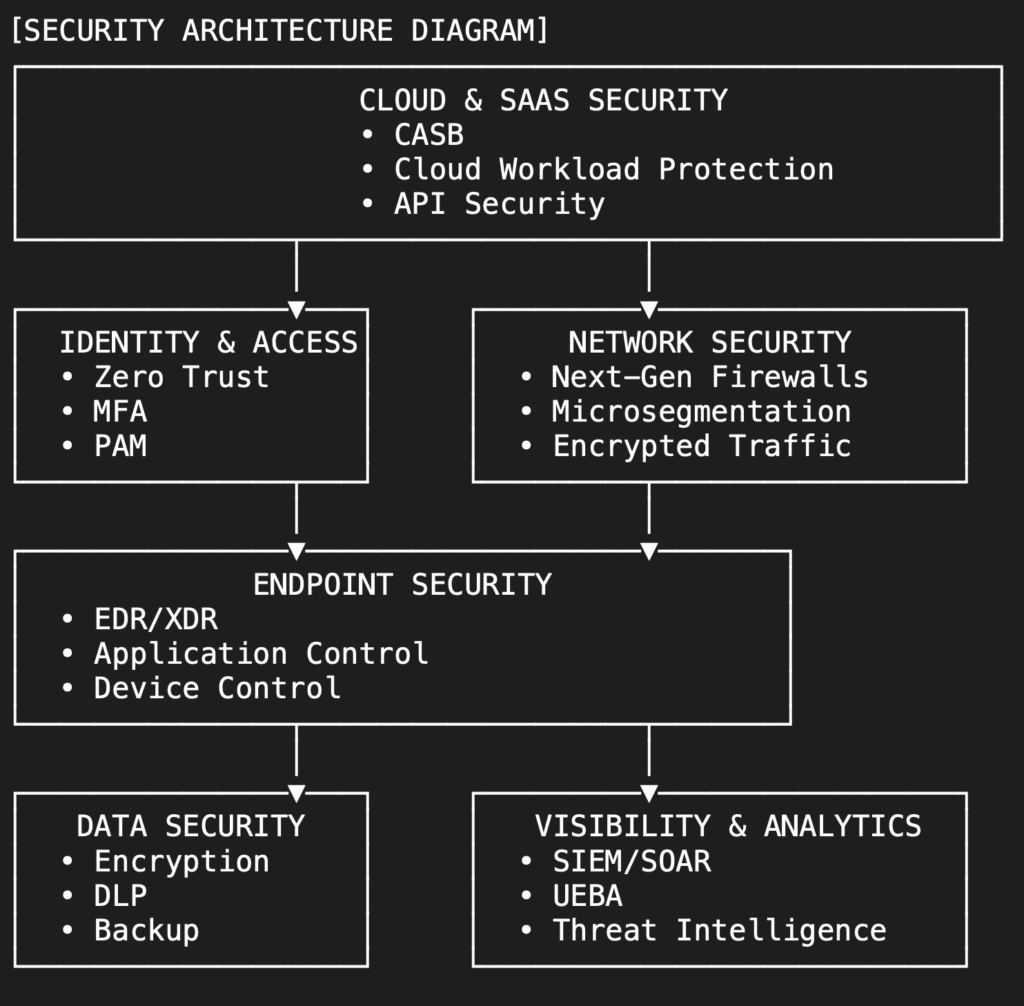
Key Architectural Components
- Identity & Access Layer (The New Perimeter)
- Implements Zero Trust principles (never trust, always verify)
- Enforces Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all users
- Manages Privileged Access (PAM) with just-in-time credentials
- Network Security Layer
- Next-Gen Firewalls with deep packet inspection
- Microsegmentation to limit lateral movement
- Encrypted traffic analysis to detect hidden threats
- Endpoint Security Layer
- EDR/XDR solutions for advanced threat detection
- Application control to prevent unauthorised software
- Device policies to manage USB/removable media
- Data Security Layer
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to monitor sensitive data
- Immutable backups stored air-gapped from networks
- Visibility & Analytics Layer
- SIEM for centralised log collection and analysis
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
- Threat intelligence integration for proactive defense
How This Architecture Prevents Attacks
- Against Ransomware:
- EDR detects malicious activity
- Microsegmentation contains spread
- Immutable backups enable recovery
- Against Phishing:
- MFA prevents credential theft
- Email filtering blocks malicious messages
- UEBA detects anomalous login behavior
- Against Supply Chain Attacks:
- Zero Trust limits third-party access
- Network segmentation contains damage
- SIEM correlates unusual activity
4. Real-World Cyber Attacks
High-Impact Attacks (Severe Consequences)
- UK Co-op Ransomware Attack – Retail operations disrupted nationwide
- UK Electoral Commission Hack – 40 million voter records exposed
- MOVEit Transfer Mass Exploitation – 2,500+ organizations compromised globally
- Medibank Australia Data Breach – 9.7 million medical records stolen
- Colonial Pipeline Ransomware – Caused fuel shortages across US East Coast
- SolarWinds Orion Compromise – Russian APT infiltrated 18,000 organizations
Medium-Impact Attacks (Significant Damage)
7. Marks & Spencer Employee Breach – Staff PII exposed
8. T-Mobile API Breach – 37 million customer accounts compromised
9. Uber Breach via Contractor – Internal systems and source code accessed
10. Kaseya VSA Supply Chain – 1,500+ businesses affected via MSP software
11. Magellan Health Ransomware – 365,000 patient records exposed
12. EasyJet Customer Breach – 9 million traveler records compromised
Low-Medium Impact Attacks (Contained Damage)
13. Shein $1.9M Vendor Fraud – Deepfake audio business email compromise
14. Twitter Celebrity Bitcoin Scam – High-profile account takeovers
15. Zoom Credential Stuffing – 500K accounts breached via reused passwords
5. Implementing Your Security Architecture
Phase 1: Foundation (0-3 Months)
- Deploy MFA everywhere
- Implement basic network segmentation
- Start endpoint detection (EDR)
Phase 2: Enhancement (3-6 Months)
- Roll out Zero Trust policies
- Add encrypted traffic inspection
- Conduct first architecture review
Phase 3: Maturity (6-12 Months)
- Full microsegmentation
- Automated SOAR playbooks
- Regular red team exercises
6. Emerging Cyber Threats (2024-2025)
A. AI-Powered Attacks
Attackers are using AI to craft convincing phishing emails and evade detection. Defenders must adopt AI-driven security tools to counter these threats.
B. Quantum Computing Risks
Quantum computers could break current encryption standards, necessitating post-quantum cryptography.
C. Space & Satellite Hacking
As reliance on satellite communications grows, attacks on GPS and internet satellites pose new risks.
D. 5G & IoT Exploits
The expansion of 5G and IoT devices creates a larger attack surface for botnets and DDoS attacks.
7. Key Takeaways & Action Plan
Immediate Steps
✅ Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all accounts.
✅ Patch known vulnerabilities—prioritise critical systems.
✅ Train employees on phishing and social engineering.
Mid-Term Strategy
🔵 Implement Zero Trust Architecture—verify every access request.
🔵 Conduct penetration testing to identify weaknesses.
Long-Term Resilience
🟣 Adopt AI-powered security tools for proactive threat detection.
🟣 Develop a cyber insurance policy to mitigate financial risks.
8. Conclusion: Architecture is Your Foundation
Modern cyber threats demand architectural thinking – not just point solutions. Organisations that build security into their infrastructure through:
- Zero Trust principles
- Layered defenses
- Continuous monitoring
…will be best positioned to withstand the evolving threat landscape.
Your Next Steps:
- Assess your current architecture
- Identify critical gaps
- Develop a 12-month roadmap from immediate to long-term
#CyberSecurity #ZeroTrust #SecurityArchitecture #RansomwareProtection



Leave a Reply